Supplements 101.
Supplements 101.

“Supplements can enhance a diet where there are shortfalls, but a handful of vitamin, mineral or other dietary supplements can never take the place of a healthy diet”
– American Dietetic Association (ADA)

Visiting your health food store can be overwhelming
- Before starting any supplements regimen, it’s best to consult a doctor or dietitian.
- If you eat fruits, vegetables, fish, lean meats and dairy products, you most likely do not need to take nutritional supplements
Nutritional supplements may be helpful if
- you don’t eat a balanced diet
- you are a vegetarian or vegan
- you are a woman who is pregnant or may become pregnant
- you are an adult over the age of 50
Which vitamins matter?
- There are 13 essential vitamins that your body cannot make in sufficient amounts on its own
- The way to get them is through food or supplements or in combination.
Vitamin A
- Helps vision, immunity and red blood cell development.
- How Much Do I Need:
- 5000 IU (International Units)
- Sources:
- Carrots and leafy green vegetables
Vitamin D
- Helps our bodies absorb calcium and keeping our bones healthy.
- How Much Do I Need:
- 400IU (International Units)
- Sources:
- Cereals, dairy products and fatty fish like salmon
Vitamin E
- Protector of cells and a powerful antioxidant
- How Much Do I Need:
- 30 IU (International Units)
- Sources:
- nuts, seeds, leafy greens (Avocado)
Vitamin K
- Helps clot blood and avoid excessive bleeding
- How Much Do I Need:
- 80 ug (micrograms)
- Sources:
- Greens, such as broccoli, brussels sprouts, asparagus, spinach
Vitamin C
- Growth and repair of body tissues, and is thought to help fight the common cold
- How Much Do I Need:
- 60 mg (milligrams)
- Sources:
- Most citrus fruits and vegetables
B Vitamins
- How Much Do I Need:
- B6- 2 mg
- B12- 6 micrograms
- Sources
- Poultry, fish, meat, eggs and dairy are key sources of B vitamins
- Vegetarians and vegans may consider supplementing
Calcium
- Often lacking in American diets
- How Much Do I Need:
- 1000 mg (milligrams)
- Sources:
- Dairy products, fortified foods, dark leafy greens, soybeans, beans, fish, and raisins.
Fish Oils
- Studies show that omega-3 fatty acids are cardio-protective and the basis for the American Heart Association recommendation to consume fatty fish twice weekly
- Sources
- Foods such as canola oil, soybeans, flax, walnuts and algae are all sources of omega-3s, but they are not a substitute for fatty fish.
Glucosamine and Chondroitin
- These supplements are often taken by people with joint pain.
- In a study published in the The New England Journal of Medicine, these supplements, taken alone or in combination, were not found to provide significant relief from osteoarthritis knee pain.
- About 40% of osteoarthritis patients may benefit from taking 1,500 mg of glucosamine and 1,200 mg chondroitin sulphate a day (for) four to eight weeks
What are the Risks?
- With anything you ingest, there can be risks associated.
- An overdose of vitamins A, D, E or K can even be life-threatening
- Water-soluble vitamins, such as B-complex vitamins and vitamin C, are less dangerous because they dissolve in water
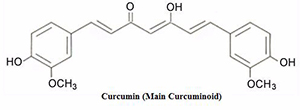
The Story of Curcumin

- Curcuminoids are powerful antioxidants and anti-inflammatories used in India for generations.
- Many Indian foods contain turmeric, of which curcumin is the main active ingredient.
- However, the curcumin content in turmeric is only about 3%
- Many chronic diseases in the USA are considered to be caused by low-level inflammation
- Coronary artery disease
- Cancer
- Obesity
- Various degenerative conditions (arthritis)
Curcuminoids are known to exist in:
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa or JiangHuang)
- Common Ginger (Zingiber officinale) and shampoo ginger (Zingiber zerumbet)
How it Works?
- Curcumin blocks NF-kB, a molecule that travels into the nuclei of cells and turns on genes related to inflammation.
- NF-kB is believed to play a major role in many chronic diseases
- Boosts the body’s own anti-oxidant pathways.
- Increase brain function by increase brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
- Effective in women to prevent heart disease
Arthritis
- Arthritis is a common disorder characterized by joint inflammation.
- Many studies show that curcumin can help treat symptoms of arthritis and is in some cases more effective than anti-inflammatories
Warning
- Curcumin may slow blood clotting, so patient taking anti-coagulants should be cautious
Dr. Singh’s Current Studies on Curcumin
- The comparative effectiveness of Curcumin vs NSAIDs for the treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis
- Comparing topical NSAID to Curcumin in the treatment of shoulder and elbow tendonitis
Bottom Line
- Supplements are not intended as food substitutes
- If you eat a fairly well-balanced diet, chances are that taking dietary supplements may not be worth the added effort or expense.
- Curcumin Dosing
- 500-1500mg daily is sufficient to produce a therapeutic benefit and avoid toxicity



Leave a Reply